Skip Navigation
You've got data. How do you start turning it into value? One answer is predictive analytics.
Predictive analytics applications parse complex data sets that integrate data from multiple sources to generate insights. You can use the predictions to make informed decisions about running or growing your business.
Descriptive analytics vs. predictive analytics vs. prescriptive analytics
The category of analytics application you choose will depend on your needs and the use case, and you may end up using more than one at a time. Three categories of analytics that companies deploy today include descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive.
- Descriptive analytics answers "what happened?" Descriptive analytics takes data and turns it into something business managers can visualize, understand, and interpret. It provides intelligence into historical performance, and answers questions about what happened. Descriptive analytics reports are designed to be run and viewed on a regular basis. Examples include customer, operations, and sales reports.
- Predictive analytics answers "what will happen?" These tools provide insights about likely future outcomes — forecasts, based on descriptive data but with added predictions using data science and often algorithms that make use of multiple data sets. The more data available, the better the predictions. Examples include sales forecasting, consumer credit scores, and retailers' suggestions for what you may want to read, view, or purchase next.
- Prescriptive analytics answers "what should we do next?" Prescriptive analytics takes predictive analytics a step further by offering advice about what actions to take. It examines possible outcomes that result from different possible actions and suggests which actions will have optimal outcomes. Creating prescriptive analytics requires advanced modeling techniques and knowledge of many analytic algorithms — all part of the job of data scientists.
You might use descriptive analytics to understand key trends in past business operations, and deploy predictive analytics to assess current trends and compare them to historical trends. You might leverage prescriptive analytics to help devise or evaluate changes you intend to make to improve the business going forward.
Try Stitch for free for 14 days
- Unlimited data volume during trial
- Set up in minutes
How predictive analytics works
The exact processes behind predictive analytics models vary. However, all predictive analytics operations follow these basic steps:
- Problem identification: Before you start your data analytics project, you should identify what problem you are trying to solve.
- Data collection: In this step, you identify the sources for your data and collect data from them.
- Data validation: You may need to prepare data for analytics by transforming it and correcting data quality issues.
- Data analysis: Once your data is ready, you can deploy an analytics tool to create models and data visualizations. Data modeling is the process of describing the structure, associations, and constraints relevant to available data, eventually encoding these rules into a reusable standard. It's an integral part of the planning stage for any analytics deployment or business intelligence project.
- Data interpretation: After you've completed analysis, you can interpret the results. Visualizations allow you to make sense of complex analytics results.
- Decision and deployment: The final step is evaluating the results of your analytics and making decisions based on them.
Rate of replication
Is real-time data replication necessary for predictive analytics? Real-time replication can degrade the performance of data warehouses, bogging down data loading and taking up processing resources that could be spent creating reports.
For most organizations and for most use cases, data that is a few minutes old is sufficiently up to date. If your company uses data analytics to give managers the information they need to make better decisions, it doesn't make sense to replicate data for your analytics tools faster than the human brain can process.
Experience replication benefits without stretching your resources
Types of predictive analytics models
You can create or deploy multiple types of models as you create predictive analytics, each of which caters to different use cases and needs. The data that you feed to the models may also be different, depending upon your goals. Here are three common types of predictive analytics models.
Classification models
A classification model, as you might expect, places items into categories.
For example, you might use a classification model to analyze social media posts that mention your company and classify each as positive or negative. You could do this using a sentiment analysis algorithm that parses the text in each message and — based on characteristics like the words and emoticons present — determines whether the poster was expressing an opinion that is primarily positive or negative (or neutral). Based on these classifications, you could decide which negative posts require a response in order to resolve a complaint, and which positive ones your marketing team could use to promote the company.
Regression models
A regression model predicts how an ongoing trend will change in the future.
For instance, a regression model could help you predict how much traffic you can expect for your online store for a particular time of day, day of the week, or season. By analyzing data about current website traffic, as well as data from periods in the past, a regression model can predict whether, for example, you can expect more or less traffic to the site for the next holiday season. This insight can help your IT team to determine how many resources to allocate to the site to meet demand. It could also help your marketing and sales teams assess the role that the site should play in their holiday campaigns.
Outlier models
An outlier model highlights anomalous figures — outliers — in a dataset.
For example, an outlier model might highlight a dramatic increase in customer support calls or product returns in a short period of time, indicating a product failure that leads to a recall. An outlier model also may be used to predict fraud by highlighting outliers in insurance claims, medical records or financial transactions.
Examples of predictive analytics in action
To understand how predictive analytics creates value in the real world, consider some common examples of predictive analytics in action:
- Financial analysis: Setting prices is challenging, especially in dynamic and competitive markets. Predictive analytics can help by using regression models to predict what customers will pay for a product or service in the future, based on data such as how much they are paying you now and how much they are paying your competitors. With this information, you'll be in a better position to know how much you should charge for a product or service in a week, a month, or a year from now, and how that pricing impacts your overall cash flow.
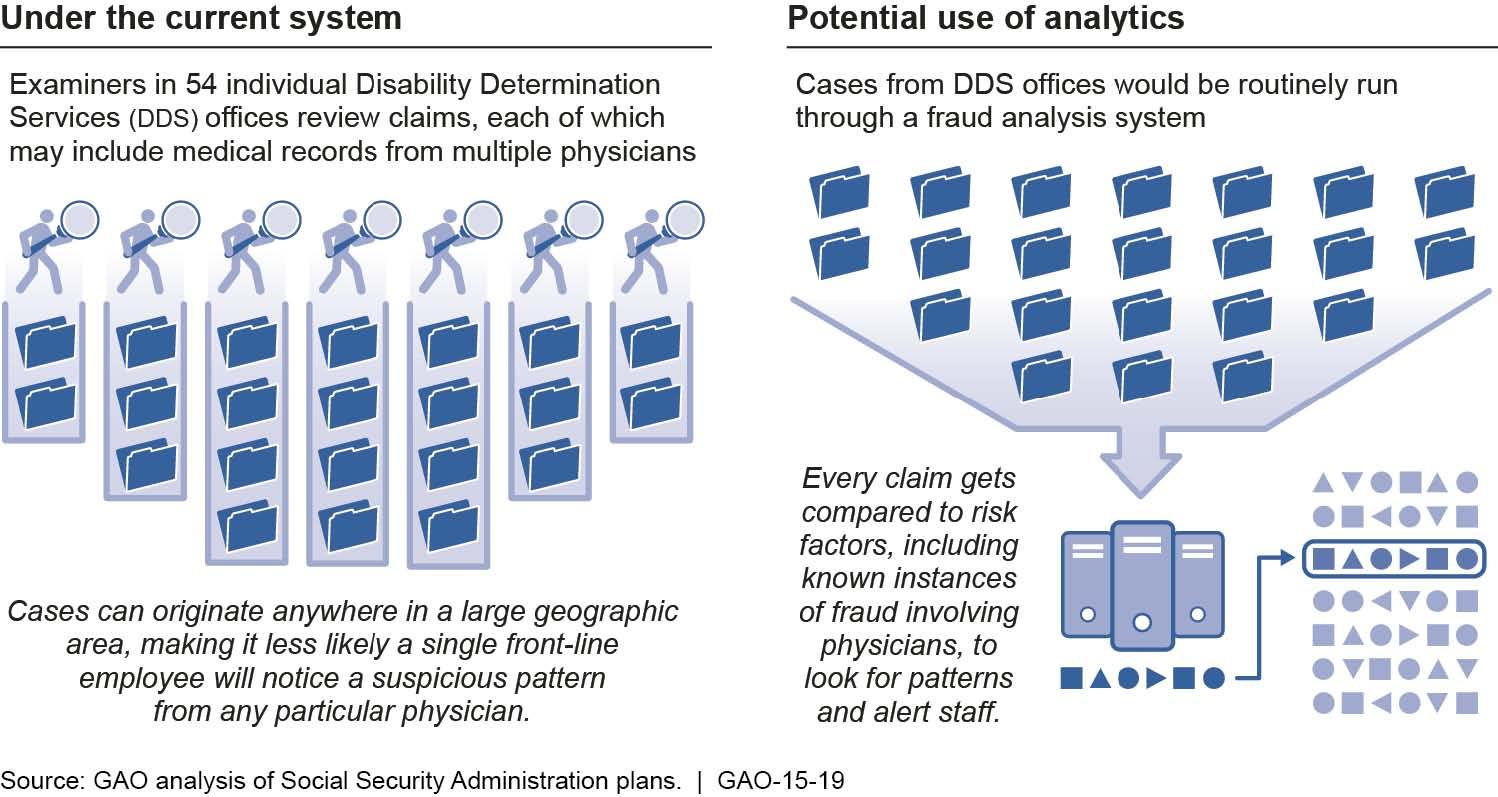
- Fraud prevention and detection: Catching fraud in real time is always better than waiting until after the fact to find out that criminals have struck. Predictive analytics can assess data associated with transactions or customers to help determine almost instantaneously whether there's a likelihood of fraud.
Example of how predictive analytics can be used to detect potential fraud
- Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity incidents, too, are something that need to be detected in real time to prevent serious damage. Predictive analytics can help by analyzing data from your IT systems and detecting anomalies — such as a rapid series of login attempts from an account that's not normally very active, or language inside email messages that's associated with phishing.
- Customer relationship management: Understanding your customers, what their preferences are, and how they change over time is hard work. Predictive analytics makes it simpler by delivering predictions about how customer needs or desires could change over time, and how they vary. For example, predictive analytics might tell you that customers of a certain age group or gender are more likely than others to purchase a certain service, or that returns are higher for people in a certain region.
Applications of predictive analytics
Many industries already use predictive analytics to help improve business outcomes.
Predictive analytics in health care
Predictive analytics offers opportunities for improving health care outcomes. Not only can it help reduce fraud and costs, it can also help with tasks such as reviewing medical imaging (by using classification models to determine whether an image suggests the presence of a problem) or assessing the risk factor of a patient becoming addicted to certain types of painkillers.
Predictive analytics in marketing
Marketers need to know what customers want, when they want it. With predictive analytics, marketing teams can assess how well online ads are performing, for example, and adjust the ads accordingly to maximize their impact. Or they can use data to help optimize the customer experience and drive more sales.
Predictive analytics in retail
From fraud detection to inventory management, predictive analytics helps retailers optimize and standardize their operations. With predictive analytics, companies can prevent fraudulent transactions, or order more of a particular item before it's sold out.
Get started with predictive analytics
Predictive analytics starts with determining which data you need to support the model or models to use for your business, then building a data pipeline to bring that data into a single repository against which you can run your analytics.
The Stitch solution is simple, straightforward, and ready to go right out of the box. You can assemble a data pipeline in the cloud and get connected to your favorite analytics tools in minutes. So, set up a free trial today, and make more of your data available for analysis more quickly.
Give Stitch a try, on us
Stitch streams all of your data directly to your analytics warehouse.
Set up in minutesUnlimited data volume during trial